
Under the research program at Leal, we research the HVAC&R field for the development of the Indian HVAC&R Industry
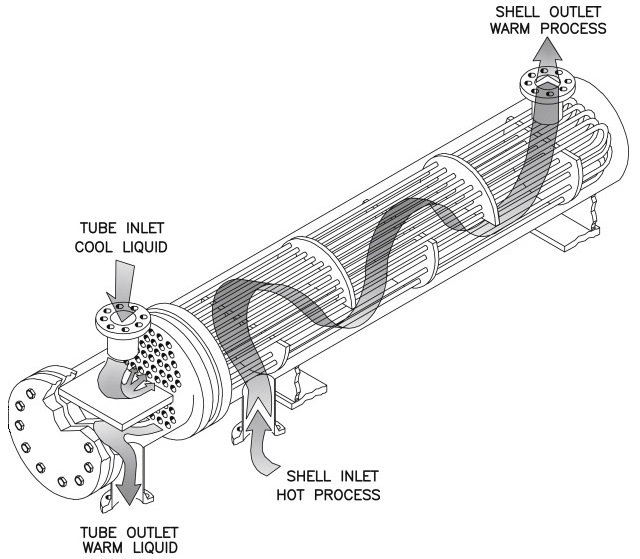
Shell and Tube Evaporator and Condenser
As heat exchangers are an inseparable part of the HVAC industry, we at LEAL SOFTWARE SOLUTION PVT. LTD. is about to develop software for shell and tube heat exchanger manufacturers that will help them to design a suitable heat exchanger as per the application and requirement, this can only be achieved by research and development for which our design team is taking rigorous efforts and maintaining the standards mentioned by TEMA and other organization.
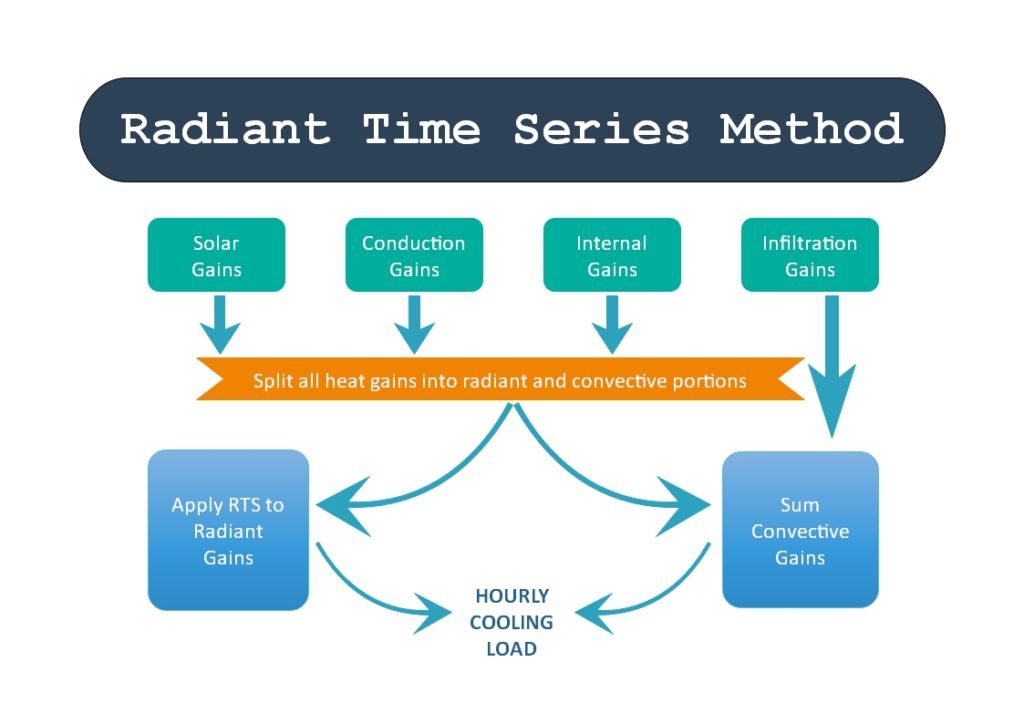

Radiant time series method for Indian condition
The radiant time series (RTS) method is a simplified method for performing design cooling load calculations that are derived from the heat balance (HB) method. It effectively replaces all other simplified (non-heat-balance) methods, such as the transfer function method (TFM), the cooling load temperature difference/cooling load factor (CLTD/CLF) method, and the total equivalent temperature difference/time averaging (TETD/TA) method. This method was developed to offer an approach that is rigorous, yet does not require iterative calculations, and that quantifies each component’s contribution to the total cooling load. In addition, it is desirable for the user to be able to inspect and compare the coefficients for different construction and zone types in a form showing their relative effect on the result. These characteristics of the RTS method make it easier to apply engineering judgment during cooling load calculation. The RTS method is suitable for peak design load calculations, but not for annual energy simulations because of its inherent limiting assumptions. Although simple in concept, RTS involves too many calculations for practical use as a manual method, although it can easily be implemented in a simple computerized spreadsheet.
Therefore we are developing Heat load Calculator software based on the RTS method for Indian conditions.
Heat load calculator using the Transfer function method.
The basic procedures for estimating the maximum design cooling load for a conditioned space were developed when all design calculations were performed manually. For this reason, extensive design analysis was not part of the primary load estimate. Today, with computers used for routine design calculations, the individual load elements may be evaluated more thoroughly and a comprehensive design analysis can be included with the results. The TFM method makes it possible to estimate the cooling load for a conditioned space on an hour-by-hour basis and to predict resultant conditions that can be expected in that space for various system types, control strategies, and operating schedules.
So for 24-hour detail heat load calculation and energy analysis, we are developing software with our research that will be affordable and efficient.

